Food safety regulators have started initiatives to teach people how to make their own French fries and chips at home to reduce their intake of acrylamide. Potatoes should be stored in the dark and fried quickly, according to the campaign's advice.
Washing

The main source of dietary acrylamide exposure is the intake of fried potato products like chips and French fries. When reducing sugars and the amino acid asparagine undergo the Maillard reaction in highly heated starchy foods like potatoes, this molecule is created.
It is advised to wash and soak potatoes for 30 to 2 hours or to blanch them in order to decrease the production of acrylamide. This will greatly reduce their sugar content and the production of acrylamide as a result.
Additionally, it's crucial to avoid putting raw potatoes in the refrigerator because doing so raises the amount of acrylamide. Instead, it is advised to keep potatoes in a cool, dark location.
Soaking

By lowering the concentration of reducing sugars and asparagine, precursors involved in the Maillard reaction in highly heated starchy foods, soaking potatoes lowers acrylamide production. It is advised to soak potatoes in cold water for 30 minutes or more, especially if they were purchased at a store.
This is because low temperatures speed up a process known as "senescent sweetening" that encourages larger acrylamide concentrations in finished potato products, lowering sugar levels during storage (Matsura-Endo et al., 2006).
The majority of respondents who made french fries at home scrubbed the potatoes before frying (47.5%) and either blanched (71.0%) or soaked them in cold water for 30 minutes to two hours. Additionally, they used olive oil for frying, which is a smart idea because it helps lower the creation of acrylamide by regulating the frying temperature. Additionally, the survey participants cleaned the frying pans after each use and added new oil. Another crucial step in preventing the production of acrylamide is to add salt. By lowering the pH of finished potatoes, salt can lower acrylamide levels.
Drying
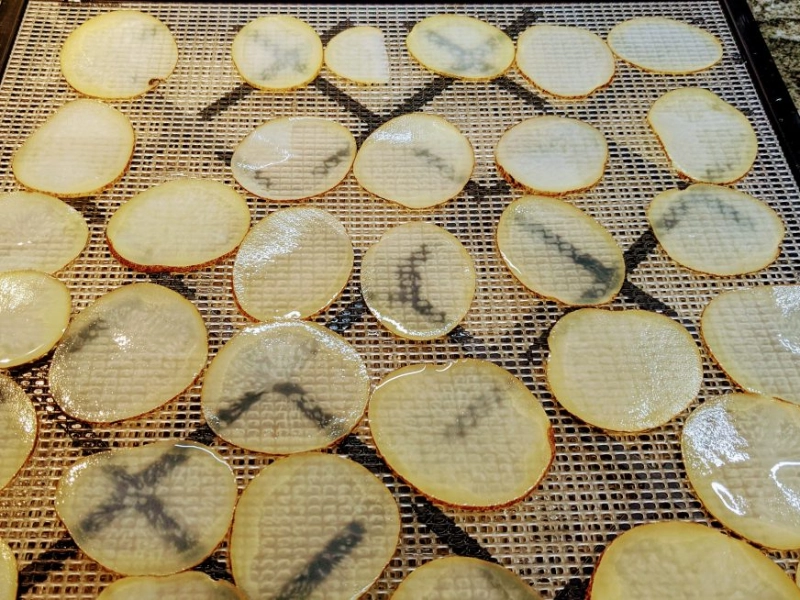

Acrylamide is a molecule that develops in highly heated starchy foods like potatoes and French fries when glucose reacts with asparagine, an amino acid. The substance has been associated with a number of health issues, including gastrointestinal and neurological complaints, and it is a possible carcinogen.
It is advised that food products be cooked to a golden colour rather than a brown one in order to decrease the development of acrylamide. This holds true for home-made fried foods like potato chips and other fried snacks. The "go for gold" campaign from the UK Food Standards Agency and the "golden but not toasted" campaign from Spain's Food Safety Authority are just two examples of the numerous efforts that national food safety agencies have undertaken with the goal of educating consumers on this subject.
Pre-treating potato slices before frying them is an additional method to lower acrylamide production. As a pretreatment, immersing and blanching potatoes effectively reduces the development of acrylamide in fried foods (Tareke et al., 2002; Becalski et al., 2003; Rydberg et al., 2003).
Storage

It has been hypothesised that keeping raw potatoes in the refrigerator increases the quantity of sugars that become acrylamide when they are cooked, roasted, or baked. A recent study claims that chilling potatoes doesn't significantly affect how much acrylamide they release when cooked.
The easiest method to lessen your exposure to acrylamide is to choose alternatives to foods made of potatoes that are high in the substance, such as French fries and potato chips. Boiling, steaming, and microwaving are also advantageous over frying, roasting, and baking. Potatoes should ideally be cooked in small batches and turned frequently if you decide to fry them. Additionally, it is suggested to stay away from meals that have been fried until they are quite brown because they frequently have the highest quantities of acrylamide. When eating toasted bread, choose a light colour rather than a medium or dark one because these have the highest acrylamide content. Click here for more details about acrylamide in food.
Advertisement
Recommended Reading: What Fruit Is Coolest For Your Body?























Minimizes interpretive variance.
Good candidate for daily review.
Provides a durable taxonomy base.
Strong pulse—where next?
This triangulates perspectives well.